Mutations are genetic variation in DNA (that are abnormal) and they can have drastic effects on the body. They affect the amino acids that are made that means that the protein could also be changed. They are errors made when DNA replication goes slightly wrong and the wrong base is imputed.
Types of Mutation
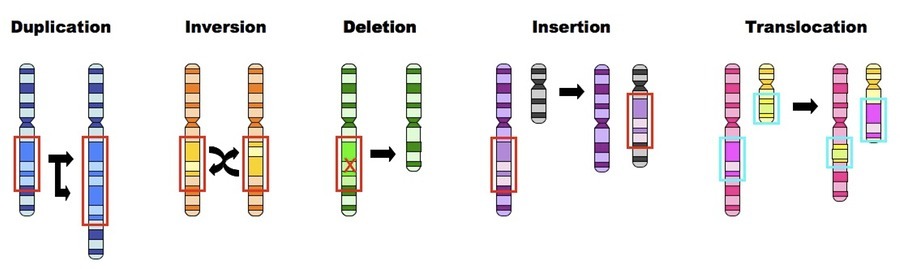
- Point mutations: deletion, addition or substitution in the nucleotides. (Deletion is when a nucleotide is missing, addition is when an extra one is added, and substitution is when a different nucleotide is added in place of something else that was supposed to be there)
- All point mutations happen during DNA replication. If not corrected, they can be passed on during cell division (and its bad)
- There are also chromosomal mutations: duplication, deletion, insertion, inversion and translocation
Genetic Variation
Sexual recombination
- independent assortment
- crossing over
- random fertilisation
Heritability (of mutations)
- germline mutations - gametes; affect offspring
- somatic mutations - body cells; doesn’t affect off spring
Speciation
- Gene flow stops (no interbreeding)
- 2 populations of some species become isolated
- -> could be geographical: allopatric speciation (e.g. a river starts running and they can’t cross anymore)
- -> Reproductive mechanisms: sympatric speciation
Divergent evolution
- 2 new species from one another
Convergent
- Different ancestor but some similar characteristics
- E.g. sharks/dolphins

